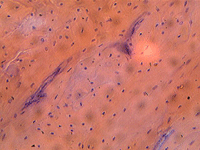
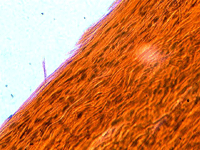
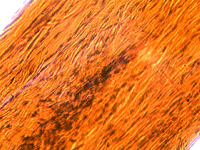
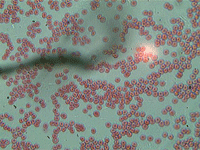
Picture Gallery
To start your microscopic study you need to put the prepared slide of your choice on the microscope’s stage and fix it with stage clips. It is recommended to begin with the objective with the lowest magnification and use it to define the area that is going to be thoroughly studied under higher magnifications.
After you have chosen the most interesting area for the observation, you need to make sure that it’s in the very center of the microscope’s field of view (move the slide on the stage if needed). Otherwise the area of interest might appear outside of the field of view after switching to objective lens with higher magnification.
You can always find lots of interesting prepared slides for microscopes in this section.
The pictures in this gallery were made with Levenhuk D50L NG Digital Microscope and the Levenhuk C35 NG digital camera installed on Rainbow 50L, 50L PLUS and D50L PLUS microscopes.
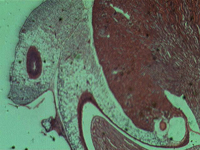
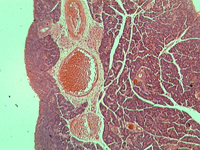
1. Rat’s kidney, longitudinal section.
In transmitted light, 80x magnification.
In transmitted light, 200x magnification.
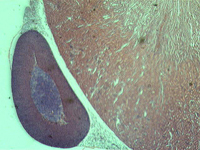
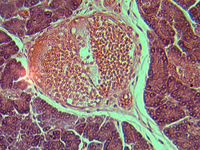
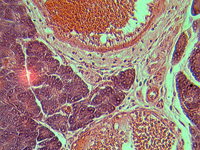
2. Section of the pancreas.
In transmitted light, 80x magnification.
In transmitted light, 200x magnification.
In transmitted light, 800x magnification.
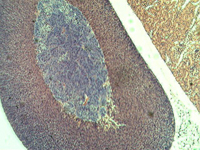
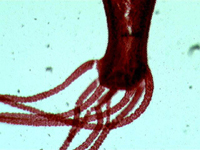
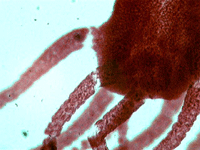
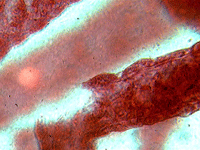
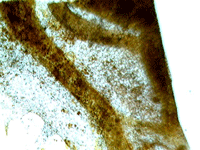
3. Hydra.
In transmitted light, 80x magnification.
In transmitted light, 200x magnification.
In transmitted light, 800x magnification.
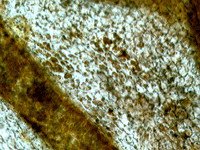
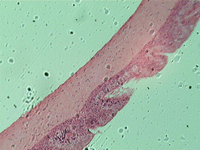
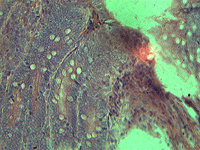
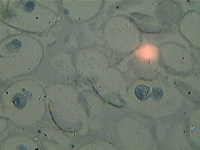
4. Simple squamous epithelium.
In transmitted light, 80x magnification.
In transmitted light, 200x magnification.
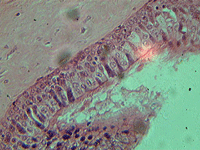
5. Ciliated epithelium section.
In transmitted light, 200x magnification.
In transmitted light, 800x magnification.
6. Stratified squamous epithelium.
In transmitted light, 200x magnification.
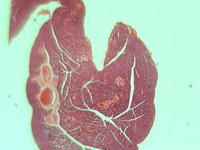
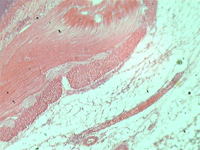
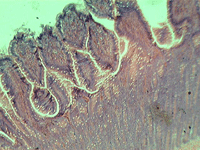
7. Cross-section of the small intestine.
In transmitted light, 200x magnification.
In transmitted light, 800x magnification.
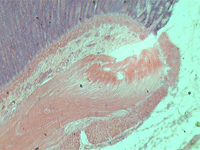
8. Section of the compact bone.
In transmitted light, 200x magnification.
In transmitted light, 800x magnification.
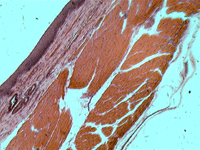
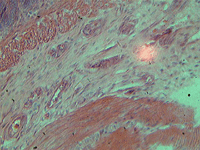
9. Section of a dog’s tendon.
In transmitted light, 800x magnification.
10. Human blood cells.
In transmitted light, 800x magnification.
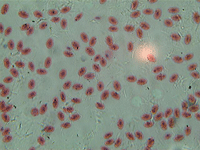
11. Fish blood cells.
In transmitted light, 800x magnification.
12. Mitosis in ascaris eggs cells.
In transmitted light, 800x magnification.
Any reproduction of the material for public publication in any information medium and in any format is prohibited. You can refer to this article with active link to eu.levenhuk.com.
The manufacturer reserves the right to make changes to the pricing, product range and specifications or discontinue products without prior notice.